LN+'s Posts
The Lightning Network: A Glimpse into 2023's Soaring Growth
Posted over 2 years ago
Transaction Volume: A Staggering Leap
- Transaction Count: An estimated lower bound of 6.6 million routed Lightning transactions was recorded in August 2023. This figure could be just the tip of the iceberg due to the inherent privacy features of the Lightning Network.
- Growth Rate: A mind-blowing 1,212% growth was observed since August 2021, where the transaction count was 503k. This growth defied the odds, even in the face of a 44% drop in Bitcoin's price.
- Transaction Speed: The Lightning Network processed an average of 2.5 transactions per second (TPS), outpacing Bitcoin's on-chain average of 4.4 TPS and marking a significant leap from the 0.2 TPS recorded in August 2021.

Dominant Use Cases
Financial Metrics: On the Rise
- Routed Amount: The Lightning Network publicly routed around $78.2 million, utilizing 5,000 BTC in capacity in August 2023.
- Annual Volume: This translates to a whopping $936 million in annual volume, utilizing $133 million in capacity. The activity on the Lightning Network even outpaces Bitcoin's on-chain velocity.
Expanding the Utility of Bitcoin

User Adoption: A Growing Force
- Monthly Active Users: An estimated 279k to 1.116 million users were actively transacting on the Lightning Network as of September 2023.
- Wallet Downloads: A staggering number of Lightning-compatible wallets, between 1.8 to 3.7 million, were downloaded, indicating the rising interest and adoption of this technology.
The Global Picture
Industry Dynamics
- Steady Infrastructure: The number of nodes, channels, and capacity on the Lightning Network has remained consistent.
- Funding: A hefty sum of $530.93 million was funneled into 39 Lightning companies between 2018 and 2022, with $428.46 million raised just in 2022.
River's Performance
Looking Ahead
Download the detailed report
BitVM: Ushering in a New Era of Bitcoin Computations
Posted over 2 years ago
The Basics of BitVM
- Instead of running computations on Bitcoin, they're verified. Think of it like the optimistic rollups you might've heard about.
- A user (called the prover) claims a particular function's outcome. If they're bluffing, another user (the verifier) can swiftly call them out with a fraud proof and even penalize them.
- The magic? ANY computable function can now be verified on Bitcoin.
Why is this a Big Deal?
- Off-chain Efficiency: Large programs can be committed off-chain, using methods like the Taproot address. This means a lot of work happens off the ledger, but the footprint on Bitcoin's chain remains tiny.
- Stealth Mode: Parties can perform complex, stateful computations without leaving any trace in the chain. Only if there's a disagreement will there be a need for on-chain execution.
Endless Possibilities
- Games: Imagine playing Chess, Go, or Poker, all verified on Bitcoin.
- Bridging Chains: It might become feasible to connect BTC with other chains.
- Prediction Markets & Novel Opcodes: The sky is the limit with what could be achieved!
Understanding Bitcoin's Limited Instruction Set
- Security: A limited instruction set reduces the attack surface. Fewer operations mean fewer potential vulnerabilities, ensuring a robust and secure environment.
- Predictability: With fewer instructions, the behavior of the protocol is more predictable, reducing unexpected outcomes or network issues.
- Simplicity: Keeping it simple means fewer chances of bugs, making it easier for developers to understand, implement, and maintain.
BitVM's Role: Breaking Boundaries While Keeping the Fort Tight
- Verification Over Execution: BitVM doesn't execute complex computations on-chain. It merely verifies them. This distinction ensures that Bitcoin's chain remains as secure and predictable as ever.
- Off-Chain Magic: Most of the heavy lifting with BitVM happens off-chain, preserving the simplicity and security of the Bitcoin protocol. Only in cases of disputes do we see on-chain action.
The Best of Both Worlds
- Maintain Bitcoin's Core Values: The benefits of a limited instruction set—security, predictability, and simplicity—remain intact.
- Unlock New Possibilities: BitVM opens up a realm of possibilities previously thought to be out of reach for Bitcoin, from intricate games to bridging with other chains.
Challenges Ahead
In Conclusion
To learn more, read the BitVM white paper!
Taproot and the Bright Future of Bitcoin's Lightning Network
Posted over 2 years ago
What is Taproot?
- Improved Privacy: Taproot ensures that on-chain, every transaction—whether a simple transfer or a multifaceted smart contract—appears identical. This uniformity masks transaction types, thus bolstering user privacy.
- Enhanced Scalability and Efficiency: By optimizing how transaction data is stored and retrieved, Taproot renders transactions faster and more cost-effective.
- Increased Flexibility: Incorporating the Schnorr signature scheme (via BIP 340), Taproot allows for intricate smart contracts on Bitcoin without disclosing unnecessary details.
How Does Taproot Impact the Lightning Network?
- Economical Lightning Channel Transactions: Taproot's efficiency ensures that opening and closing Lightning channels are more affordable. When channels are initiated or concluded, they need to record transactions on the primary Bitcoin blockchain. With Taproot's optimizations, these transactions require less blockchain space, thus reducing fees.
- Privacy Enhancements: Traditionally, when Lightning channels were opened or closed, keen-eyed blockchain observers could spot them. With Taproot's standardizing transaction appearances, pinpointing these specific transactions becomes a daunting task. This level of discretion is a boon for privacy-focused Lightning users.
- Advanced Contractual Capabilities: Taproot's added versatility means that more intricate contracts can be integrated within Lightning channels. This expansion opens up an array of potential use cases for the Lightning Network.
In Conclusion
Current State of Taproot on Lightning
Unlocking the Mysteries of Lightning Channel Settings
Posted over 2 years ago
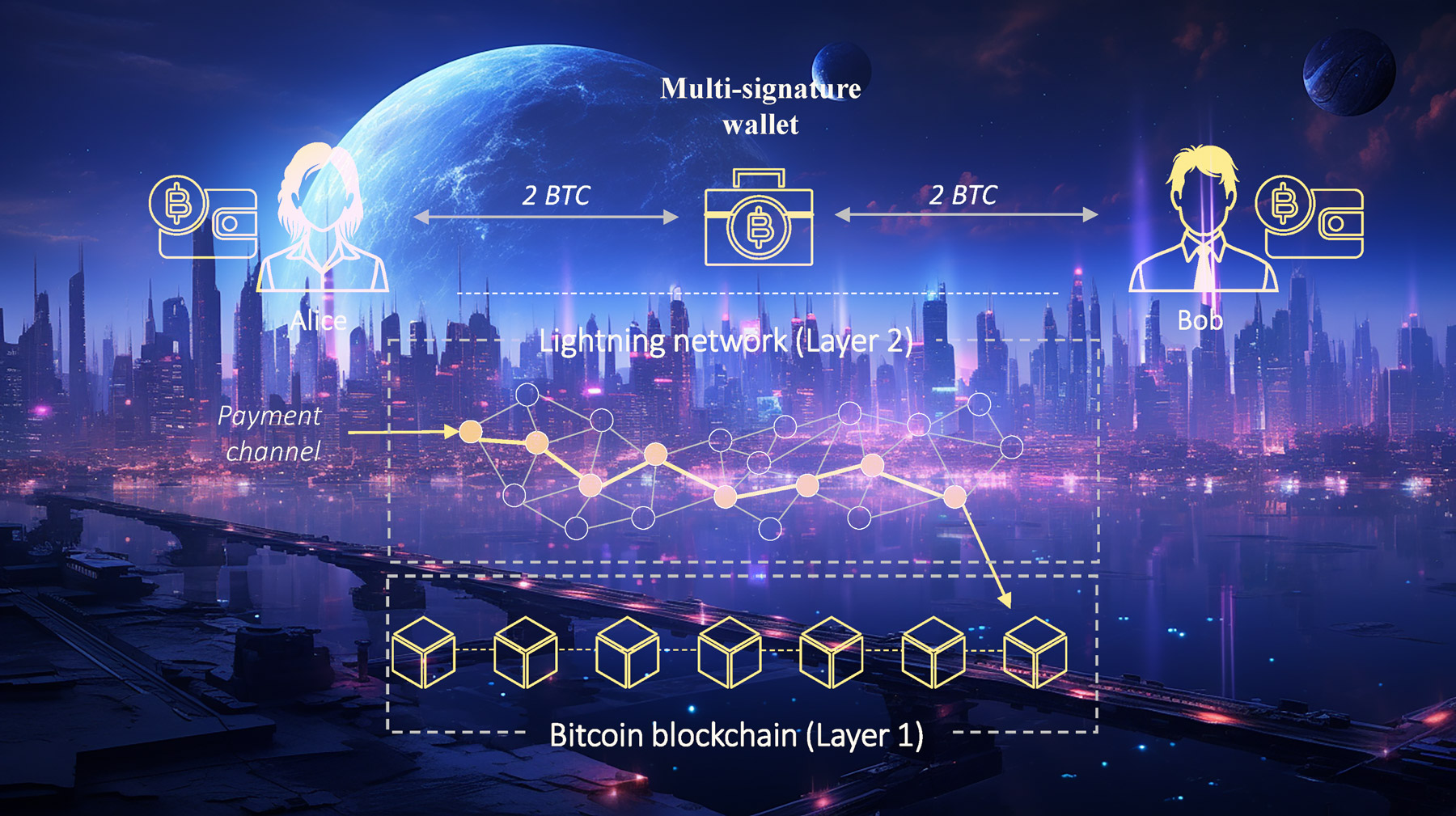
Before diving deep, it's crucial to grasp some foundational aspects of the Lightning Network. In the Lightning Network, payments between two parties take place off-chain, meaning they aren't immediately reflected on the Bitcoin blockchain until the channel concludes, either through closure or settlement. This off-chain approach allows for rapid, low-cost transactions by eliminating the need to record every transaction on the blockchain. However, for this system to work securely, the Lightning Network employs HTLCs (Hashed Time-Locked Contracts). HTLCs act as a safety mechanism, temporarily locking funds and offering a window during which these funds can be claimed or returned, depending on whether conditions are met. This locking mechanism leverages Bitcoin's scripting capabilities, especially the CheckLockTimeVerify (CLTV) function. Additionally, as payments traverse through various channels to reach their destination (routing), node operators can impose fees, making channel and fee management a vital component for effective Lightning Network operations.
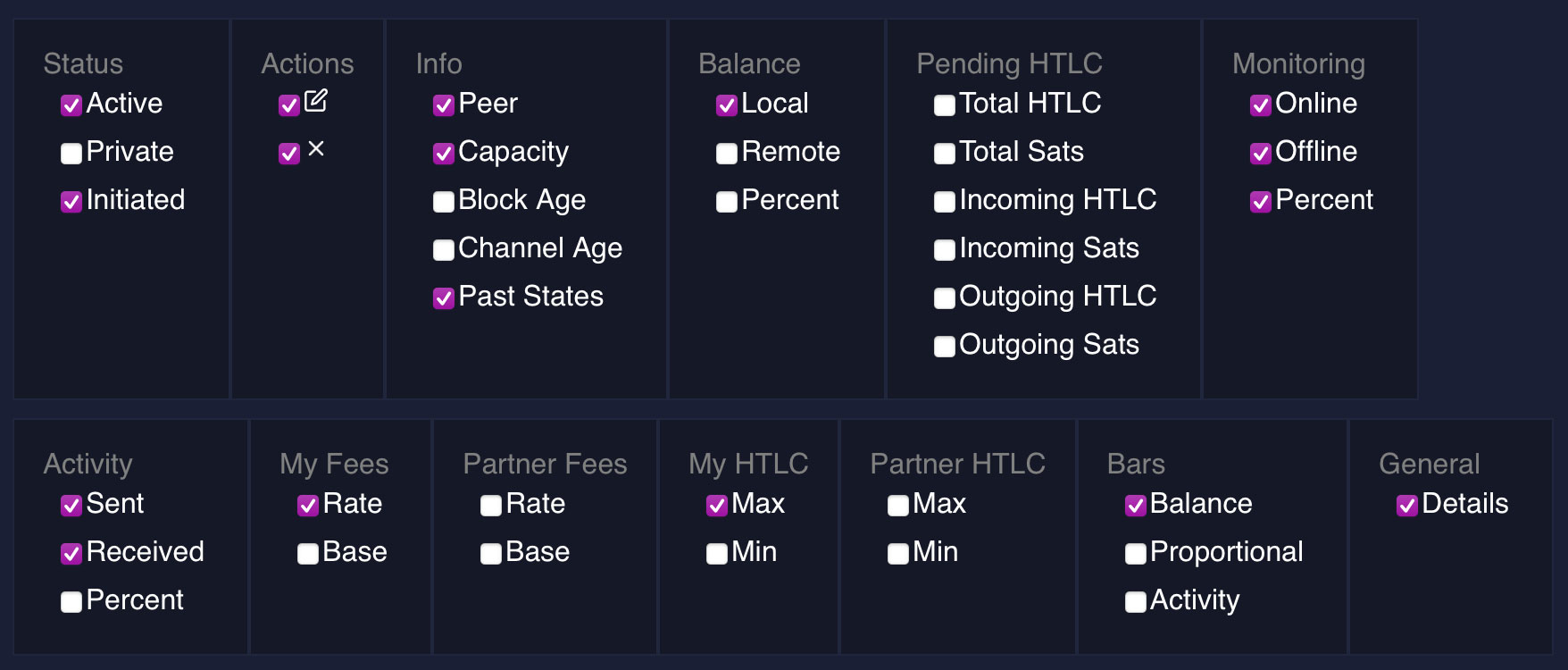
Status
- Active: Indicates whether the channel is active or inactive. An active channel means it can process transactions. If it's inactive for a long time, you should consider force closing the channel to ensure the funds are not lost if both ends of the channel happen to go offline.
- Private: If a channel is private, it's not announced to the entire Lightning Network. This means others cannot see it and make routing decisions based on its presence. Private channels do not participate in routing and thus, do not earn you routing fees. On the upside other nodes can't drain them either.
- Initiated: This denotes which party initiated the channel creation, whether it was you or your peer. This is important because the initiator pays the closing fees as well.
Actions
- Edit: Allows you to change certain aspects of the channel.
- Close: Enables you to close the channel, ending your connection and settling your balance on the main Bitcoin blockchain. When possible always close cooperatively. Only force close if the other node is offline for a long time, because force closing will lock the funds for a certain period of time.
Info
- Peer: Displays the node with which you've established this channel.
- Capacity: The total amount of Bitcoin that this channel can handle.
- Block Age: Shows how many blocks have been added to the Bitcoin blockchain since this channel was opened.
- Channel Age: Displays the actual time duration since the channel was opened. Older channels are more trusted by certain routing algorithms and they are also a source of pride for some lightning network operators proving the thesis that channels can stay open for a long time moving funds back and force hundreds of times.
- Past States: Indicates the number of times the channel's state has been updated. This includes successful and unsuccessful attempts to route. The larger the number the more space the channel takes on your disk. Some lightning network operators like to close channels that have accumulated a huge amount of past states (ex. 1,000,000+).
Balance
- Local: Amount of bitcoin on your side of the channel. This is how much you can spend from it.
- Remote: Amount of Bitcoin owned by your peer in this channel. This is how much you can receive on it.
- Percent: Represents the proportion of the channel's capacity that you own.
Pending HTLC
- Total HTLC: The number of Hashed Time-Locked Contracts currently pending. Every time you pay, receive, or route you create an HTLC contract.
- Total Sats: Total amount in Satoshis that's in pending HTLCs.
- Incoming HTLC: Number of incoming pending transactions.
- Incoming Sats: Amount in Satoshis of incoming pending transactions.
- Outgoing HTLC: Number of outgoing pending transactions.
- Outgoing Sats: Amount in Satoshis of outgoing pending transactions.
Monitoring
- Online: Shows how long your channel peer has been online.
- Offline: Shows how long your channel peer has been offline.
- Percent: Percentage of time the peer has been online. The higher the better.
Activity
- Sent: Amount you've sent through this channel.
- Received: Amount you've received through this channel.
- Percent: Represents the proportion of the channel's activity. Over time, this value closes in on 50%.
My Fees
- Rate: The rate at which you charge fees for transactions processed through your channel. Node operators often play around with this value to find the most optimal number where they can earn the most amount of fees.
- Base: A fixed amount of fees you charge for any transaction regardless of its size. Many node operators like to set this to zero, to encourage routing algorithms choose this channel for routing smaller amounts.
Partner Fees
- Rate: The rate at which your partner charges fees for transactions processed through your channel. You can't change this, it's up to your partner.
- Base: A fixed amount your partner charges for any transaction. Also up to your partner.
My HTLC
- Max: The maximum amount in Satoshis your partner is willing to lock in a single HTLC.
- Min: The minimum amount in Satoshis your partner is willing to lock in a single HTLC.
Partner HTLC
- Max: The maximum amount in Satoshis your partner is willing to lock in a single HTLC.
- Min: The minimum amount in Satoshis your partner is willing to lock in a single HTLC.
Bars
- Balance: A visual representation of the channel's balance between you and your peer.
- Proportional: Same as above but the scale is comparatively shown to other channels.
- Activity: A visual representation of the transaction activity on this channel. The higher the number the more active the channel and thus likely generates more earnings for you through routing.
General
- Details: Gives you a button to be able to adjust many of the settings above and also the value CLTV Delta.
CLTV Delta (CheckLockTimeVerify Delta) is a term used in the Lightning Network context. It represents the number of blocks between when a commitment transaction is confirmed and when the HTLC (Hashed Time-Locked Contract) output becomes spendable. The CLTV Delta is a safety margin. It ensures that if there's a need to close a channel and submit the transaction to the blockchain (for example, in the event of a dispute), there's sufficient time to do so before the HTLC expires. This is crucial for the Lightning Network's security. If the CLTV Delta is too small, there's a risk that a transaction might not be confirmed in time, which could result in loss of funds. Therefore, node operators on the Lightning Network often set a CLTV Delta of several blocks to ensure there's enough time for transactions to be processed in worst-case scenarios.
Understanding these settings and terms gives you a better grasp of how the Lightning Network operates and helps you manage your channels more effectively. Whether you're routing payments for others or using the network for your transactions, it's essential to be aware of what each setting signifies. Always remember to monitor and adjust your channels to ensure smooth transactions and maintain good relationships with your peers. Happy Lightning Networking!
I'm a Lightning Network Maximalist and Here's Why
Posted over 2 years ago
Bitcoin: The Unwavering Foundation
Why Not Just Be a Bitcoin Maximalist?
The Lightning Network: Supercharging Bitcoin
Why the Lightning Network Resonates with Me
- Focused Innovation: Instead of trying to reinvent the wheel or claim to be "the next Bitcoin," the Lightning Network focuses on enhancing what Bitcoin already offers. It's an example of targeted, meaningful innovation.
- Network Effects and Longevity: Just as Bitcoin benefits from the network effect (its value increases as more people adopt it), the same applies to the Lightning Network. Its growing adoption as the primary Layer 2 solution for Bitcoin makes it more robust and valuable. And as it continues to exist and serve its purpose effectively, the Lindy effect suggests a promising future for the Lightning Network.
- Decentralization and Security: The Lightning Network doesn't compromise on the core tenets of Bitcoin. It remains decentralized, and while operating mostly off-chain, it still leans on the underlying security of the Bitcoin blockchain.
While I deeply respect and believe in the foundational principles and potential of Bitcoin, and I'm very interested in all kinds of innovations on Bitcoin, I'm a maximalist for its most promising extension: the Lightning Network. It represents a bridge between the revolutionary principles of Bitcoin and the practical needs of a global, scalable digital currency. As both Bitcoin and the Lightning Network continue to prove their resilience and value, I'm excited about the decentralized future they're paving.
If interested, learn more about the history of LN, about LN's key benefits, and how to start an LN node of your own.
Posted over 2 years ago
- Liquidity Pool Participation Control: There's now a checkbox for you to opt in or out of the Liquidity Pool. So, if you wish to momentarily stop receiving offers even when you have liquidity credits, just uncheck. With this option off, your node will remain hidden from the pool, and your profile won't display your liquidity credits or the "Open Channel" button. Stay tuned—more Liquidity Pool enhancements are on the way!
- Custom Node Text Color: Personalize the text color on your node profile page's header, buttons, and social images. You can keep the default, which contrasts with your node color, or switch to light or dark shades. This should improve readability, especially if you've got custom background images on your node profile header.
- Hide Beginner Guides: Feel like an expert? On your node profile, you'll find an option to hide the beginner help sections present on the Liquidity Swaps, Liquidity Pool, and Watch Swaps pages. Toggle this off to declutter and zero in on key details.
- YouTube Integration for News: Spice up your news updates! You can now add a YouTube video to your news updates.
- Simplified Capacity Reading: When initiating a Liquidity Swap or a Pool Credit Transaction, we'll provide an interpretation of the Satoshi amount you input, so no more counting zeros. For instance, typing "10000000 SAT" will also display as "10M SAT / 0.1 BTC."
- Enhanced Help Text: We've refined the guidance texts across the site for clarity and comprehension.
Your feedback is invaluable. If you have any feature requests or come across any glitches, please drop a comment. I'm listening!
LNbits Release 0.11.0: Welcome the LNbits Node Manager
Posted over 2 years ago
Performance Enhancements
A Special Mention
Diving into the LNbits Node Manager
- Channel Management: Gone are the days of relying on extraneous tools or processes. With the LNbits Node Manager, handling Lightning channels is straightforward, all from within LNbits.
- Transaction History: Transparency is key. Users can now effortlessly view their node's transaction history, showcasing a detailed list of all inbound and outbound payments.
- Public Node Page: For those looking to expand their network, the Node Manager has a public node page feature. This simplifies the process for others wishing to establish a channel with your node.
- Activation Simplicity: Engaging with these new features is a breeze. Just activate the node UI via the LNbits admin panel, and you're all set!

Future Prospects
LNbits release 0.11.0, or Leo, is not just another software update. It signifies LNbits' drive for innovation, enhancement, and most importantly, empowering the Bitcoin Lightning Network ecosystem. The LNbits Node Manager is here, and it promises to redefine convenience and efficiency.
The Future of Money Movement: A Deep Dive with David Marcus of Lightspark
Posted over 2 years ago
Most fintech enthusiasts might recall David's name from his involvement as the spearhead of Facebook’s ambitious Libra/Diem project, which, although now defunct, was a testament to his commitment towards streamlining global financial transactions.
On the recent episode of Fintech One-on-One, David discusses his journey and vision for the future of payments:
- A Tech Maven: David’s extensive experience in the tech world sets a foundation for his current aspirations.
- The Facebook Journey: We delved into the inception and evolution of the Libra/Diem project and what it aimed to achieve.
- Birth of Lightspark: After Facebook, David channeled his energies to found Lightspark, a platform poised to revolutionize money transfers.
- The Lightning Network: A significant portion was dedicated to explaining the intricacies of the Lightning Network – a layer that operates atop Bitcoin.
- Lightspark’s Affinity for Lightning: David discussed the reasons for choosing the Lightning Network as their technological base.
- Lightspark Unveiled: We got a clearer picture of Lightspark's operations, partnerships, and its target demographic.
- The Current User Base: Lightspark's technology already boasts a userbase, which David touched upon.
- Performance Metrics: How many transactions can Lightspark handle in a second? The numbers might surprise you!
- Navigating Micropayments: David’s take on simplifying and making micropayments more efficient was enlightening.
- Regulatory Labyrinths: The journey to scaling isn't without challenges, especially when regulations come into play.
- Lightspark - A Different Rail: David emphasized viewing Lightspark as an alternative payment methodology rather than a rival.
- Beyond Crypto: While based on blockchain technology, Lightspark’s mission transcends cryptocurrency.
- Infinite Possibilities: From e-commerce to personal transactions, the potential applications of Lightspark are vast.
- Programmable Money: David's views on the future, where money can be programmed just like software, were truly futuristic.
- Internet-like Payments: David envisions a payment system as open, instantaneous, and interoperable as the internet.
- Global Footprint: Lightspark isn’t confined to one region – they're already making waves globally.
- Revenue Streams: A sneak peek into how Lightspark monetizes its cutting-edge solutions.
- Last-mile Power: The synergy of real-time payments with Lightning is a game-changer, especially for the crucial last-mile transactions.
- Commerce of the Future: Imagine a world with instantaneous global payments. David did, and he believes it's the path forward.
David Marcus' passion and conviction in creating a robust global payment network are contagious. If you're as intrigued as I am by the future of fintech, Lightspark is undoubtedly a venture to watch. Dive deeper into these insights by tuning into the Fintech One-on-One podcast!
Rust-Lightning v0.0.117: Steering towards asynchronous channel monitoring and beyond
Posted over 2 years ago
- ProbabilisticScorer Improvement: The internal models of ProbabilisticScorer were significantly improved to boost payment success rates, albeit at a small cost to routefinding performance. This was achieved through better decaying, a more detailed historical channel liquidity tracker, and a new default option to estimate a channel's current liquidity non-linearly based on its capacity.
- Custom TLVs for HTLC Recipients: This update allows the addition of custom TLVs (Type-Length-Value) for recipients of Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs), enhancing the protocol's flexibility.
- Third-Party Watchtowers Support: The ability to generate transactions for third-party watchtowers was added, providing an extra layer of security and oversight over channel operations.
- KVStore Interface: The KVStorePersister was replaced with a more generic KVStore interface, bringing more features and flexibility.
- Batch Funding of Outbound Channels: A new method for batch funding of outbound channels was introduced, optimizing the process of channel establishment.
- Payment Path Probing: Before approving a payment, users can now probe potential payment paths using ChannelManager::send_preflight_probes.
- Asynchronous ChannelMonitor Updating: In an alpha preview, fully asynchronous ChannelMonitor updating was introduced. However, it's noted that there are a few known but rare race conditions which might lead to a loss of funds.
LND 0.17.0 Beta Release: Taproot Channels and Faster Syncs
Posted over 2 years ago
Introduction of Simple Taproot Channels
- LND becomes the inaugural Lightning protocol to present Taproot channels, facilitating superior on-chain privacy and cost efficiency.
- These channels merge the efficiency of Schnorr signatures with Taproot, making on-chain operations more space- and cost-efficient.
- In the initial phase, these channels are unadvertised. Public Taproot channels are on the horizon with the development of Gossip 1.75.
Lightning Speeds with Neutrino
- Neutrino, a Bitcoin light client tailored for mobile Lightning nodes, now syncs faster than ever.
- Syncing nodes is now 400x quicker, thanks to improvements in filter fetching and storage. Filters are batch-fetched in groups of 1,000, slashing sync time.
Revamped Watchtowers
- The new update introduces disk persistence for the watchtower client, minimizing memory usage and amplifying reliability.
- Pending updates from removed tower sessions are now reallocated to other sessions, ensuring the consistent delivery of updates.
Looking Ahead
- Upcoming versions promise more advancements based on Taproot Channels, such as Taproot Asset Channels and the integration of Gossip 1.75.
- These developments hint at a brighter future for Bitcoin, merging the best of Taproot – privacy, cost-efficiency, and script versatility – with the Lightning Network.
Demystifying the Lightning Network's Potential
Posted over 2 years ago
The Lightning Network in a Nutshell
How the Lightning Network is Changing the Game
- Cross-Border Transactions: Think of remittance payments, where billions are lost annually due to transaction fees. The LN can significantly cut down these costs. By swiftly converting currencies through Bitcoin, LN can enable quick and inexpensive funds transfer globally.
- IoT & Machine-to-Machine Payments: The Internet of Things (IoT) holds vast potential, but monetizing it has been a challenge. The LN introduces a straightforward micropayment system. Imagine an autonomous taxi that pays for its charging or a smart fridge that handles its electricity bill.
- Decentralized Exchanges: Centralized exchanges have been vulnerable to hacks, leading to massive financial losses. LN can bolster decentralized exchanges, eliminating the need to trust central entities with user funds.
- Digital Assets Transfers: Beyond Bitcoin, LN facilitates the transfer of other digital tokens, like stablecoins. Using protocols such as RGB, the LN makes token transfers more scalable and confidential.
- Ecosystem Growth: Several companies and service providers, like Zap, BlueWallet, and Bitrefill, are building around the LN, contributing to a robust ecosystem. From merchants to gaming app developers, a diverse array of stakeholders is capitalizing on the LN's capabilities.
Challenges Ahead
Looking to the Future
Read the full study!
Understanding Bitcoin Lightning Network forwarding
Posted over 2 years ago
Forwarding: A Vital Cog in the LN Machine
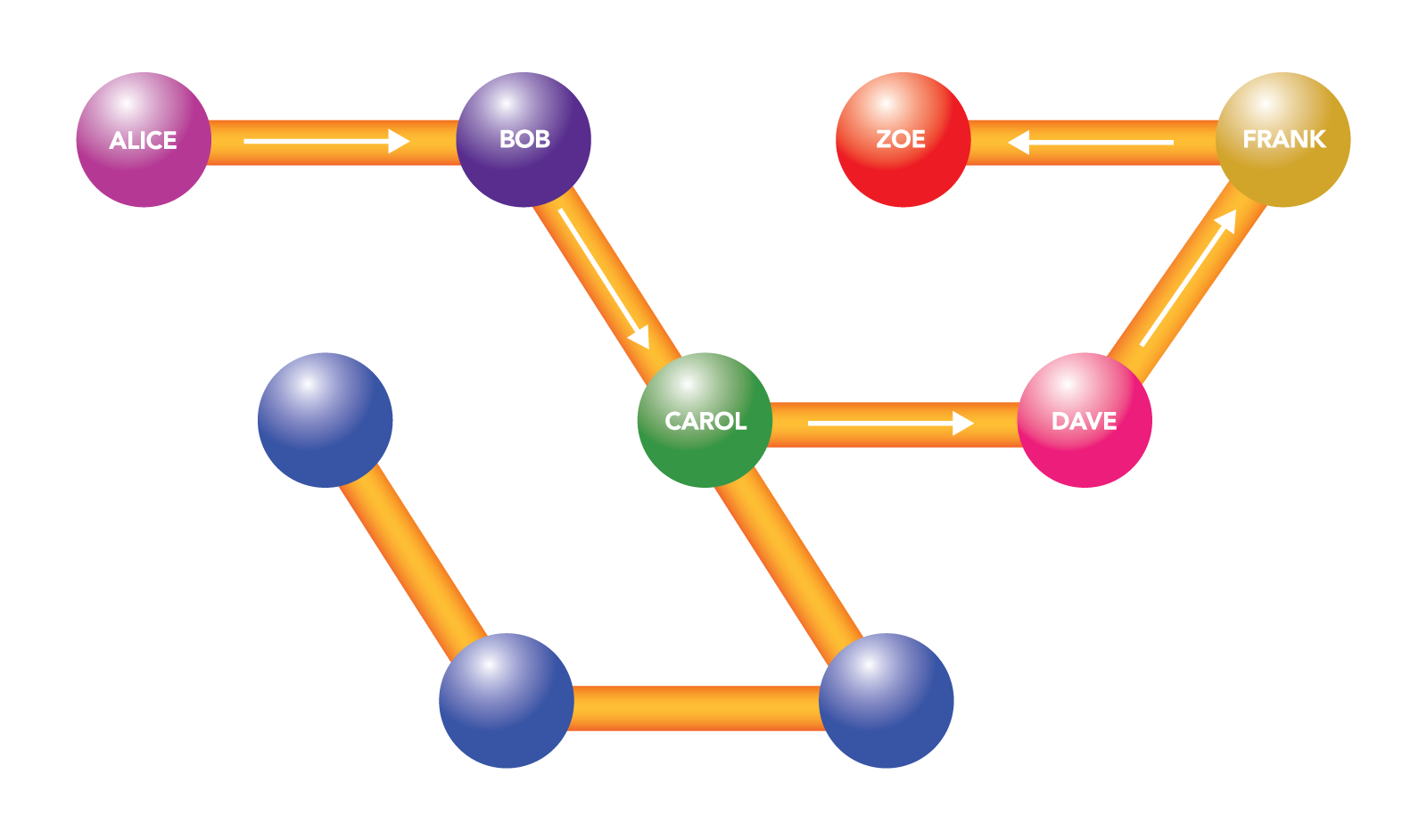
Imagine Alice wants to send payments to Zoe, but they don’t have a direct channel between them. If Alice has a channel with Bob, and Bob has a channel with Carol, who in turn has a channel with Dave, and Dave has a channel with Frank, and Frank has a channel with Zoe, then Alice can forward her payment through Bob, Carol, Dave and Frank to get to Zoe.
The Role of Public Channels in Forwarding
The Cost of Forwarding: Two Types of Fees
- Base Fee: This is a fixed fee that a node charges for every payment it forwards, irrespective of the payment amount.
- Fee Rate (or Proportional Fee): This fee is proportional to the amount being forwarded. For example, if a node charges a fee rate of 1,000 ppm (parts per million), then for every 1 Bitcoin it forwards, it will charge 0.001 Bitcoin.
The total fee for forwarding a payment is a combination of these two fees. Different nodes can set their own fees, leading to a competitive marketplace for routing payments.
Reasons Why a Forwarding Request May Fail
- Insufficient Funds in Channels: The most common reason is that one of the intermediary channels doesn’t have enough funds on the sending side. For instance, if Alice is trying to send funds through Bob to Charlie, but Bob doesn't have enough funds in his channel with Charlie, the payment will fail.
- Channel Capacity: Even if funds are available, a channel might not have the required capacity to handle a large payment. Payments on the Lightning Network can't exceed the capacity of the smallest channel in their route.
- Fee Mismatch: If the total fee required by intermediaries is more than the fee provided by the sender, the forwarding request can fail.
- Channel Closure: If one of the channels in the route gets closed while the payment is in transit, the payment will not go through.
- Route Unavailability: The Lightning Network tries to find the shortest and cheapest path for the payment. If no route is found that can handle the payment size or if all possible routes are exhausted, the payment fails.
- Node Unreliability: If one of the nodes in the chosen path is frequently offline or unstable, it can lead to payment failure.
- HTLC Limits: The Lightning Network uses Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) for secure fund transfers. There's a limit to how many concurrent HTLCs a channel can have. If this limit is reached, the channel can't forward any more payments until some of the current ones are settled.
- Time Locks Expiry: Payments in the Lightning Network are locked for a certain time duration to ensure security. If the payment isn’t completed within this time frame (perhaps due to long routes or slow nodes), it will fail.
- Privacy Concerns: Some nodes, due to privacy concerns, might reject payments that originate from or are destined to certain nodes, causing a forwarding failure.
Strategies to Maximize Earnings on a Node
- Optimal Channel Balancing: Regularly monitor and balance your channels. If a channel is imbalanced (e.g., most funds are on one side), it may not be able to forward many payments. Using tools and services that help in rebalancing can be advantageous. However if you have a channel that always forwards only one way, balancing may not be necessary and even disadvantageous. Check each channel individually to see what kind of behaviour they demonstrate.
- Competitive Fee Setting: Set your fees at competitive rates. If they're too high, users might opt for cheaper routes. If they're too low, you might not make a worthwhile profit. Monitoring the network's average fees can guide your pricing.
- Strategic Channel Openings: Open channels with well-connected and active nodes. This increases the chances of your node being in the path of payment routes. However, large nodes are already well connected so you are competing with other channels that can handle the forwarding already. Smaller nodes could be a good source of traffic, especially if they are operated by active economic actors, like stores, payment systems, etc.
- Uptime is Key: Ensure your node is online and reliable. If it frequently goes offline or is unstable, it will be less likely to be chosen for forwarding payments.
By understanding the intricacies of forwarding on the Lightning Network, one can better appreciate its decentralized and dynamic nature. Whether you're a casual user or a node operator looking to maximize profits, a deep dive into forwarding reveals yet another layer of the LN's innovative approach to scaling Bitcoin.