Latest Highlighted News
Introducing LN+ Pro Membership: Elevate Your Node to New Heights
Posted almost 2 years ago by LN+
MicroStrategy's Impact and Potential in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
Posted almost 2 years ago by LN+
Neutronpay Expands to Southeast Asia, Harnessing Lightning Network for Advanced Payment Solutions
Posted almost 2 years ago by LN+
What the Drop in Lightning Nodes Means for LN's Future?
Posted almost 2 years ago by LN+
Understanding the Lightning Network - Where Did My Sats Go?
Posted almost 2 years ago by LN+
What is a Bitcoin Lightning Network Channel Backup and How To Use It?
Posted about 2 years ago by LN+
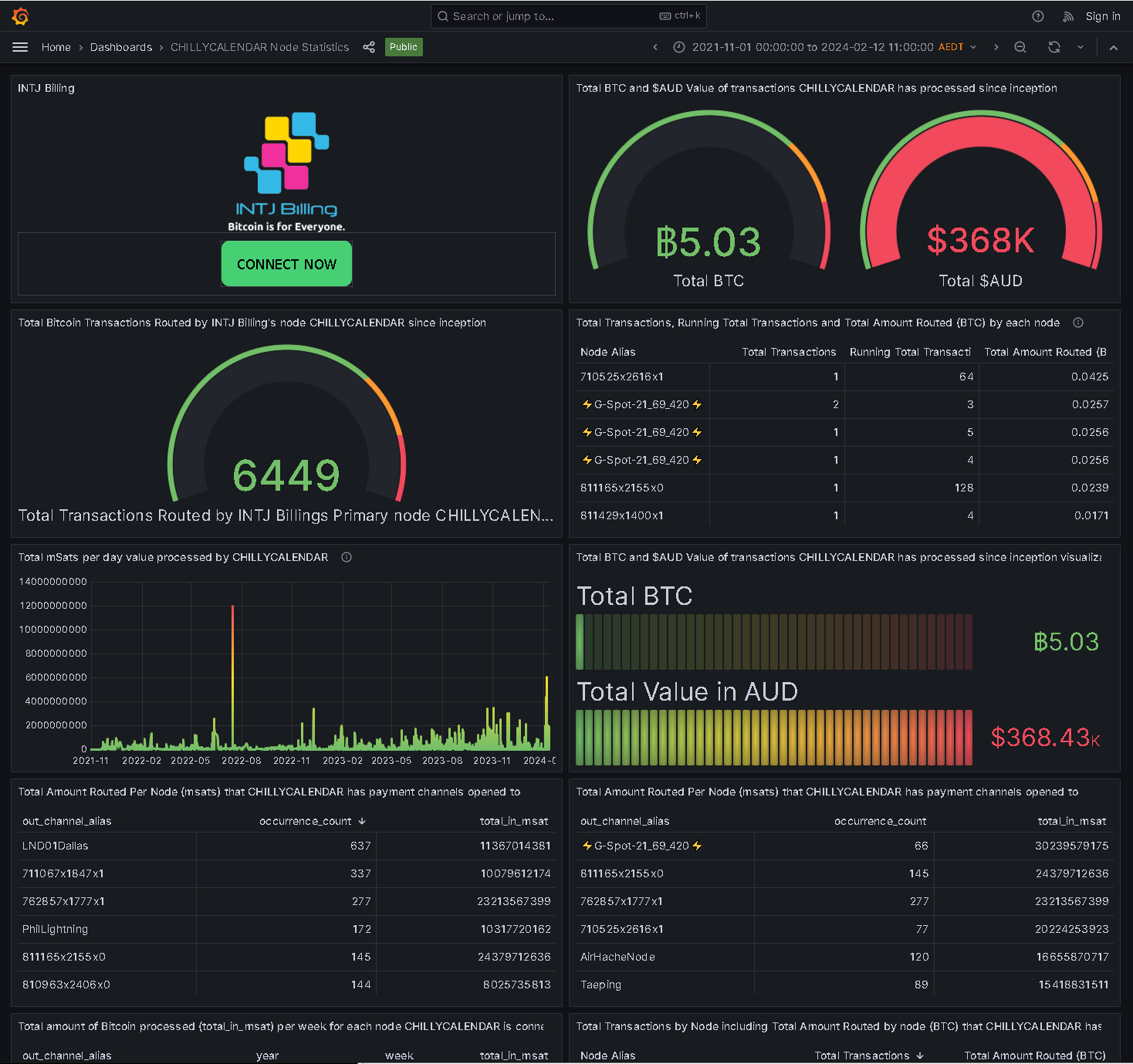
The INTJ Billing Bitcoin Lightning Network Grafana Dashboard
Posted about 2 years ago by CHILLYCALENDAR
A Guide for Situations Where Your Lightning Close-Transaction Fails to Close the Channel
Posted about 2 years ago by HODLmeTight
Simple Introduction to Understanding Elliptic Curve Cryptography in Bitcoin
Posted about 2 years ago by LN+
I'm working on building up capacity on this my secondary node CHILLYCALENDAR2
Posted about 2 years ago by CHILLYCALENDAR2